Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ashida, Takashi; ; Sato, Haruo; ; Kitamura, Akira; Kawamura, Kazuhiro
JNC TN8400 99-083, 63 Pages, 1999/11
Studies on the chemical and migration behaviour of radionuclides were carried out in the Quantitative Assessment Radionuclide Migration Experimental Facility (QUALITY)for assuring the relaiability and for improving the propriety of data concerning nuclide migration used in the Second Progress Report for the geoloical disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Five studies for solubility, sorption and diffusion concerning nuclide migration were carried out. The overview of each study and the result is as follows: (1)Study on Effect of Carbonate on Np Solubility. Solubilities of Np(IV) were measured as functions of pH and carbonate concentration under reducing conditions. The obtained data could be well described by considering two hydroxo-carbonate complexes, and those stability constants were estimated and compared with the literature data. Consequently, the data obtained in this study were similar to the literature data. (2)Study on Effect of Carbonate on Np Sorption on Bentonite. Distribution coefficients (Kd) of Np(IV) on smectite were measured as a function of carbonate concentration. The obtained Kd values were approximately constant over the carbonate concentration (total carbon concentration 0.04-0.15M). The results of desorption tests by 1M KCl and HCl at the end of sorption experiments showed two different desorption behaviour; Np(IV) was well removed by HCl for the experiments in low carbonate concentration and by KCl for those in high carbonate concentration. (3)Distribution Coefficient Measurements for Cs, Pb and Cm on Rocks. Distribution Coefficients for Cs, Pb and Cm on Japanese major rocks (basalt, mudstone, sandstone, granodiorite and tuff) were measured as a function of ionic strength. The obtained Kd values were either the same orders or higher compared with data used to both fresh and saline groundwater systems in the Second Progress Report. This indicates that the Kd data used in the Second Progress Report are either proper or conservative. ...
Oda, Chie; Arthur, R. C,*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Shibata, Masahiro; Yui, Mikazu; Neyama, Atsushi*
JNC TN8400 99-079, 287 Pages, 1999/09
Two thermodynamic databases for geochemical calculations supporting research and development on geological disposal concepts for high level radioactive waste are described in this report. One, SPRONS.JNC, is compatible with thermodynamic relations comprising the SUPCRT model and software, which permits calculation of the standard molal and partial molal thermodynamic properties of minerals, gases, aqueous species and reactions from 1 to 5000 bars and 0 to 1000 C. This database includes standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard molal entropies and volumes, and Maier-Kelly heat capacity coefficients at the reference pressure (1 bar) and temperature (25
C. This database includes standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard molal entropies and volumes, and Maier-Kelly heat capacity coefficients at the reference pressure (1 bar) and temperature (25 C) for 195 minerals and 16 gases. It also includes standard partial molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard partial molal entropies, and Helgeson, Kirkham and Flowers (HKF) equation-of-state coefficients at the reference pressure and temperature for 1147 inorganic and organic aqueous ions and complexes. SPRONS.JNC extends similar databases described elsewhere by incorporating new and revised data published in the peer-reviewed literature since 1991. The other database, PHREEQE.JNC, is compatible with the PHREEQE series of geochemical modeling codes. It includes equilibrium constants at 25
C) for 195 minerals and 16 gases. It also includes standard partial molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation, standard partial molal entropies, and Helgeson, Kirkham and Flowers (HKF) equation-of-state coefficients at the reference pressure and temperature for 1147 inorganic and organic aqueous ions and complexes. SPRONS.JNC extends similar databases described elsewhere by incorporating new and revised data published in the peer-reviewed literature since 1991. The other database, PHREEQE.JNC, is compatible with the PHREEQE series of geochemical modeling codes. It includes equilibrium constants at 25 C and 1 bar for mineral-dissolution, gas-solubility, aqueous-association and oxidation-reduction reactions. Reaction enthalpies, or coefficients in an empirical log K(T) function, are also included in this database, which permits calculation of equilibrium constants between 0 and 100
C and 1 bar for mineral-dissolution, gas-solubility, aqueous-association and oxidation-reduction reactions. Reaction enthalpies, or coefficients in an empirical log K(T) function, are also included in this database, which permits calculation of equilibrium constants between 0 and 100 C at 1 bar. All equilibrium constants, reaction enthalpies, and logK(T) coefficients in PHREEQE.JNC are calculated usig SUPCRT and SPRONS.JNC, which ensures that these two databases are mutually consistent. They are also internally consistent insofar as all the data are compatible with basic thermodynamic definitions and functional relations in the SUPCRT ...
C at 1 bar. All equilibrium constants, reaction enthalpies, and logK(T) coefficients in PHREEQE.JNC are calculated usig SUPCRT and SPRONS.JNC, which ensures that these two databases are mutually consistent. They are also internally consistent insofar as all the data are compatible with basic thermodynamic definitions and functional relations in the SUPCRT ...
Morita, Koji; Tobita, Yoshiharu; kondo, Satoru; E.A.Fischer*
JNC TN9400 2000-005, 57 Pages, 1999/05
An improved analytic equation-of-state (EOS) model using flexible thermodynamic functions is developed for a reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III. The present EOS model is designed to have adequate accuracy in describing thermodynamic properties of reactor-core materials over wide temperature and pressure ranges and to consistently satisfy basic thermodynamic relationships without deterioration of the computing efficiency. The fluid-dynamic algorithm for pressure iteration consistently coupled with the EOS model is also described in the present report. The EOS data of the basic core materials, uranium dioxide, mixed-oxide fuel, stainless steel, and sodium, are developed up to the critical point by compiling the most up-to-date and reliable sources using basic thermodynamic relationships. The thermodynamic consistency and accuracy of the evaluated EOS data are also discussed by comparison with the available sources.
Morita, Koji; Tobita, Yoshiharu; kondo, Satoru; E.A.Fischer*
JNC TN9400 2000-004, 38 Pages, 1999/05
An analytic thermophysical property model using general function forms is developed for a reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III. The function forms arc designed to represent correct behavior of properties of reactor-core materials over wide temperature ranges, especially for the thermal conductivity and the viscosity near the critical point. The most up-to-date and reliable sources for uranium dioxide, mixed-oxide fuel, stainless stee1, and sodium available at present are used to determine parameters in the proposed functions. This model is also designed to be consistent with a SIMMER-III model on thermodynamic properties and equations of state for reactor-corc materials.
Oda, Chie; *
JNC TN8400 98-001, 14 Pages, 1998/11
Solubilities of amorphous stannic oxide, SnO (am) in Na-ClO
(am) in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH
aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH , Cl
, Cl and SO
and SO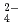 on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl
on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl , SO
, SO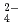 concentrations were observed in Na-ClO
concentrations were observed in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO
aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO (am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.
(am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.
PNC TN9410 97-058, 61 Pages, 1997/06
A benchmark exercise on "Tee junction of Liquid Metal Fast Reactor (LMFR) secondary circuit" was proposed by France in the scope of the said Coordinated Research Program (CRP) via International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). The physical phenomenon chosen here deals with the mixture of two flows of different temperature. ln a LMFR, several areas of the reactor are submitted to this problem. They are often difficult to design, because of the complexity of the phenomena involved. This is one of the major problems of the LMFRs. This problem has been encountered in the Phenix reactor on the secondaly loop, where defects in a tee junction zone were detected during a campaign of inspections after an operation of 90,000 hours of the reactor. The present benchmark is based on an industrial problem and deal with thermal striping phenomena. Problems on pipes induced by thermal striping phenomena have been observed in some reactors and experimental facilities coolant circuits. This report presents numerical results on thermohydraulic characteristics of the benchmark problem, carried out using a direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3 and a boundary element code BEMSET. From the analysis with both the codes, it was confirmed that the hot sodium from the small pipe rise into the cold sodium of the main pipe with thermally instabilities. Furthermore, it was indicated that the coolant mixing region including the instabilities agrees approximately with the result by eye inspections.
Terai, Takayuki*
PNC TJ9602 97-002, 75 Pages, 1997/03
Nuclear materials are often utilized under severe conditions such as high temperature, thermal transient, irradiation, corrosion by liquid metal, particle implantation, electric field and magnetic field, and an investigation on the behavior of the materials is strongly required. However, the property change is so complicated by cooperative effects of these conditions that there have been few studies on it. This project aims to clarify degradation mechanism of ceramics under the complex conditions and to contribute to the development of new advanced ceramics and surface modification. For such purposes, (1)to clarify the change in microstructure, composition and crystal structure of ceramics, (2)to analyze the distribution and condition of radiation defects and implanted ions, (3)to measure physical properties such as electric conductivity and (4)to investigate chemical and mechanical property change due to corrosion are to be carried out. In FY 1996, compatibility of several kinds of ceramic coating materials with liquid metals such as molten lithium and lithium-lead alloy (Li17-Pb83) and electrical resistivity change of these materials in the presence of the liquid metals were investigated. As a result, most of the results were in good agreement with a thermodynamic prediction and most of the compounds maintained their high electrical resistivity even in the presence of liquid lithium and lithium-lead alloy. In addition, it was pointed out that in case of Y O
O , a complex compound (LiYO
, a complex compound (LiYO ) and a non-stoichiometric compound (Y
) and a non-stoichiometric compound (Y O
O ) were formed, which was out of the thermodynamic prediction.
) were formed, which was out of the thermodynamic prediction.
L.J.Porter*; S.Yip*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; ; M.Tang*
Journal of Applied Physics, 81(1), p.96 - 106, 1997/01
Times Cited Count:69 Percentile:92.4(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
*;
PNC TN9410 96-102, 40 Pages, 1996/04
In designing the shield plug of LMFBR, it is important to evaluate the thermal response between the cover gas thermal-hydraulics and the temperature fields of the shield plug at the same time. Based on the experiments which were performed by OEC, the natural convection and the thermal radiation in the cover gas layer were calculated with the structure simulating the shield plug in a detail two-dimensional model. The calculations were carried out for 8 kinds of experimental RUNs using a FLUSH code. The main results were as follows: (1)For these 8 kinds of experimental RUNs, the velocity and the temperature distributions in the cover gas layer were presented. The radial and axial temperature distributions in the rotating plug were also presented, which were difficult to measure by the experiments. (2)The boundary surface temperature between the cover gas layer and the rotating plug had the same tendencies and the calculated average temperatures on the boundary surface had good agreements with the experimental data. The average relative deviations from experimental values were less than 1.3%. (3)The natural convection of the cover gas enhanced the temperature distributions in the structure. The effects of thermal radiation on the heat transfer was relatively small and it can be neglected when the temperature of the heated aluminum disk is less than 400 C.
C.
PNC TJ1281 95-008, 55 Pages, 1995/03
1. Introduction 2. Items of study 3. Prediction of Sn aqueous species and acquision of thermodynamic data 3.1 Test condition 3.2 Test method 3.3 Result 3.4 Discuion 3.5 Analysis 3.6 Conclusion 4. Acquisition of Sn distribution coefficients on bentonite, pure montmorillonite and  -FeO(OH) 4.1 Sorption test 4.4.1 Test condion 4.1.2 Method 4.1.3 Result 4.1.4 Discussion 4.1.5 Conclusion 4.2 Sequential eraction test 4.2.1 Test condition 4.2.2 Method 4.2.3 Result 4.2.4 Discussion 4.5 Conclusion 5. Mechanisms of Sn sorption onto bentonite 6. Apparent diffusion coecient in compacted bentonite 6.1 Preliminary analysis to predict diffusion of Sn inentonite 6.2 Test condition 6.3 Method 7. Conclusio
-FeO(OH) 4.1 Sorption test 4.4.1 Test condion 4.1.2 Method 4.1.3 Result 4.1.4 Discussion 4.1.5 Conclusion 4.2 Sequential eraction test 4.2.1 Test condition 4.2.2 Method 4.2.3 Result 4.2.4 Discussion 4.5 Conclusion 5. Mechanisms of Sn sorption onto bentonite 6. Apparent diffusion coecient in compacted bentonite 6.1 Preliminary analysis to predict diffusion of Sn inentonite 6.2 Test condition 6.3 Method 7. Conclusio
PNC TJ1533 94-001, 157 Pages, 1994/03
None